
Kardiyovasküler Sistem Anatomisi ve Fizyolojisi
Functions of the Heart The functions of the heart are as follows: Managing blood supply. Variations in the rate and force of heart contraction match blood flow to the changing metabolic needs of the tissues during rest, exercise, and changes in body position. Producing blood pressure.

10+ Outside Of The Heart Diagram Robhosking Diagram
Basics in anatomy and physiology of the heart Praveen Nagula Doctor at Osmania General Hospital, Afzalgunj, Hyderabad Recommended Anatomy of heart Dr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy 157.3K views • 71 slides ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF HEART sodha ranbir 34.4K views • 109 slides The conducting system of heart Idris Siddiqui

Heart Anatomy and PhysiologyReview
The heart is a hollow, muscular organ about the size of a fist. It is responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. The heart is composed of cardiac muscle, an involuntary muscle tissue that is found only within this organ. The term "cardiac" (as in cardiology) means "related to the heart" and comes
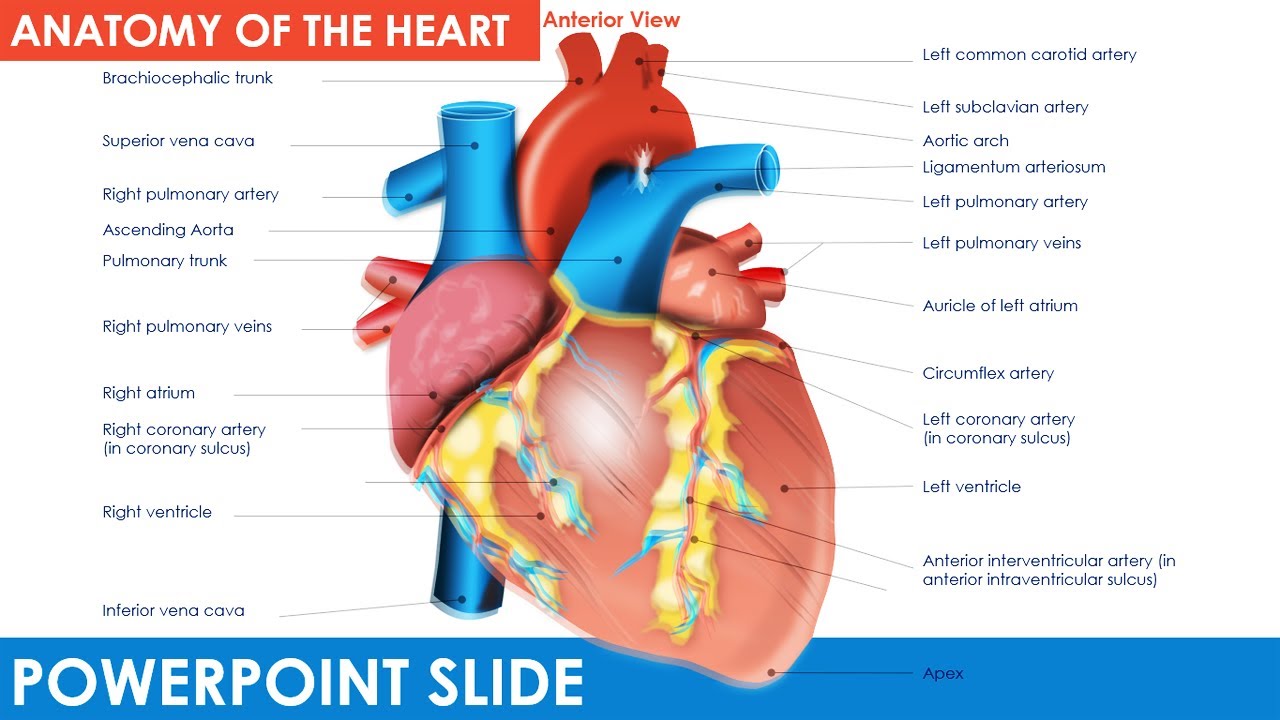
Anatomy of the Heart PowerPoint template Free Download PowerPoint University YouTube
Heart Anatomy Chambers Atria Features small, thin-walled chambers Functions receiving chambers for blood returning to the heart from the circulation push the blood into the adjacent ventricles. 10.
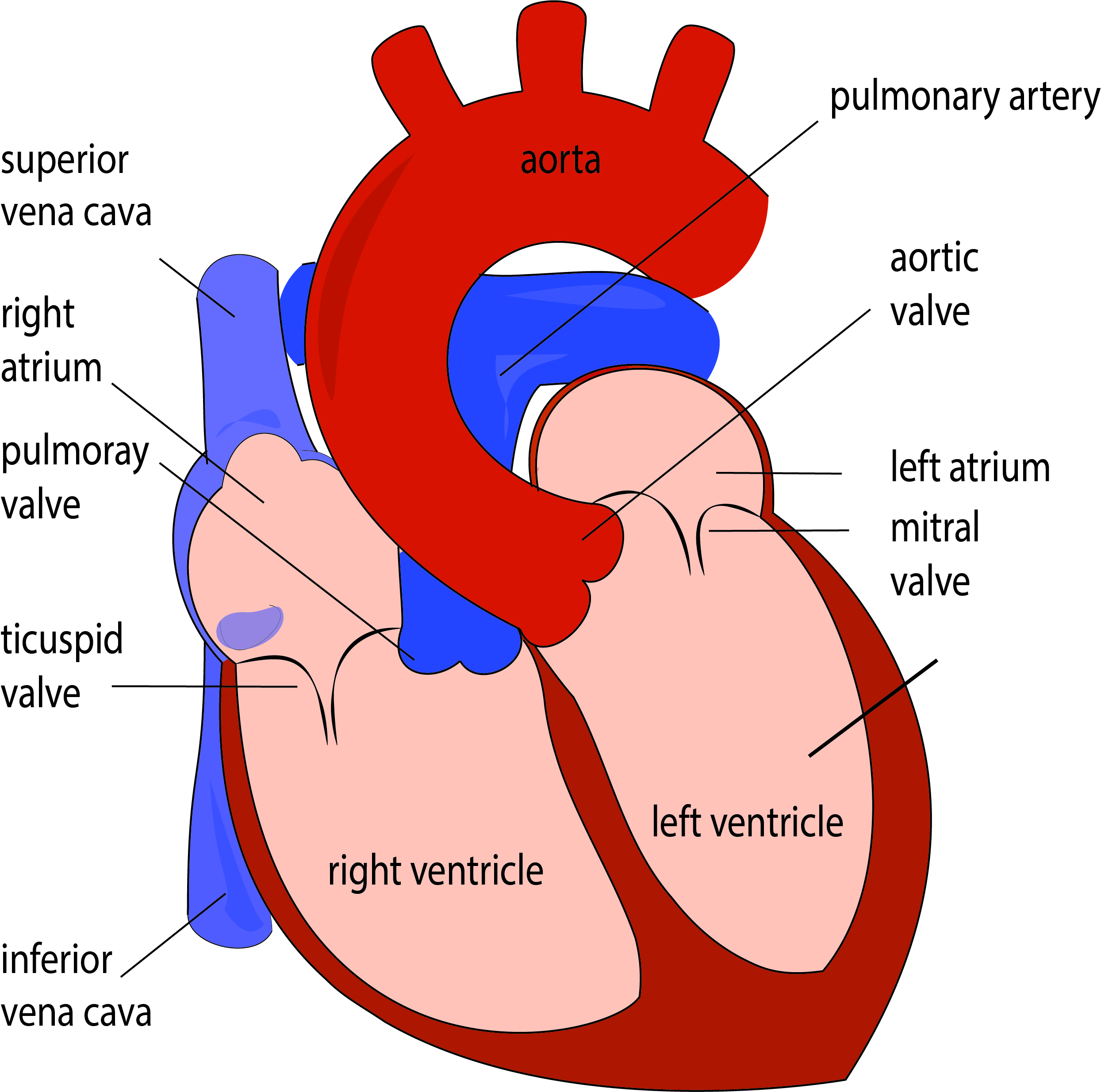
On Heart Kardiohirurgija.rs
The conducting system of heart by The conducting system of heart Idris Siddiqui 140.5K views • 26 slides Anatomy of heart by Anatomy of heart Dr. Binu Babu Nursing Lectures Incredibly Easy 158.4K views • 71 slides Cardiac conduction system by Cardiac conduction system Michael Wrock 107.1K views • 18 slides Heart Anatomy by

Heart Anatomy/Physiology
Anatomy & Physiology: BIO 161 / 162. AP BIO 161 / 162; AP 1: BIO161 Toggle Dropdown. Chapter 1: An Introduction to the Human Body ;. Heart Anatomy. PowerPoint: Chapter 19, Heart Physiology. Outline: Chapter 19, Heart Physiology. AnatomyTV Coverings Activity. Cardiac Cycle Problem Solving. Mixed Up Blood Flow Pathway. Concept Map of the Heart.

Pin on Nursing School and Study Guides
3. Functions of the cardio vascular system: • Distribution of oxygen and nutrients to all the body parts • Transportation of CO2 and metabolic waste products from tissues to lungs and other excretory organs • Distribution of water electrolytes and hormones through out the body • Part of immune system • Thermoregulation. 4.

Normal Anatomy of the Human Heart Giclee Print by Nucleus Medical Art at Chirurgia
Anatomy and physiology of heart | PPT Anatomy and physiology of heart Dec 19, 2019 • 12 likes • 2,226 views Amrutha nayaka medical student Health & Medicine A small and clear introduction of Heart Anatomy and its function. Anatomy and physiology of heart 1 of 23 Download Now Save slide Save slide Recommended
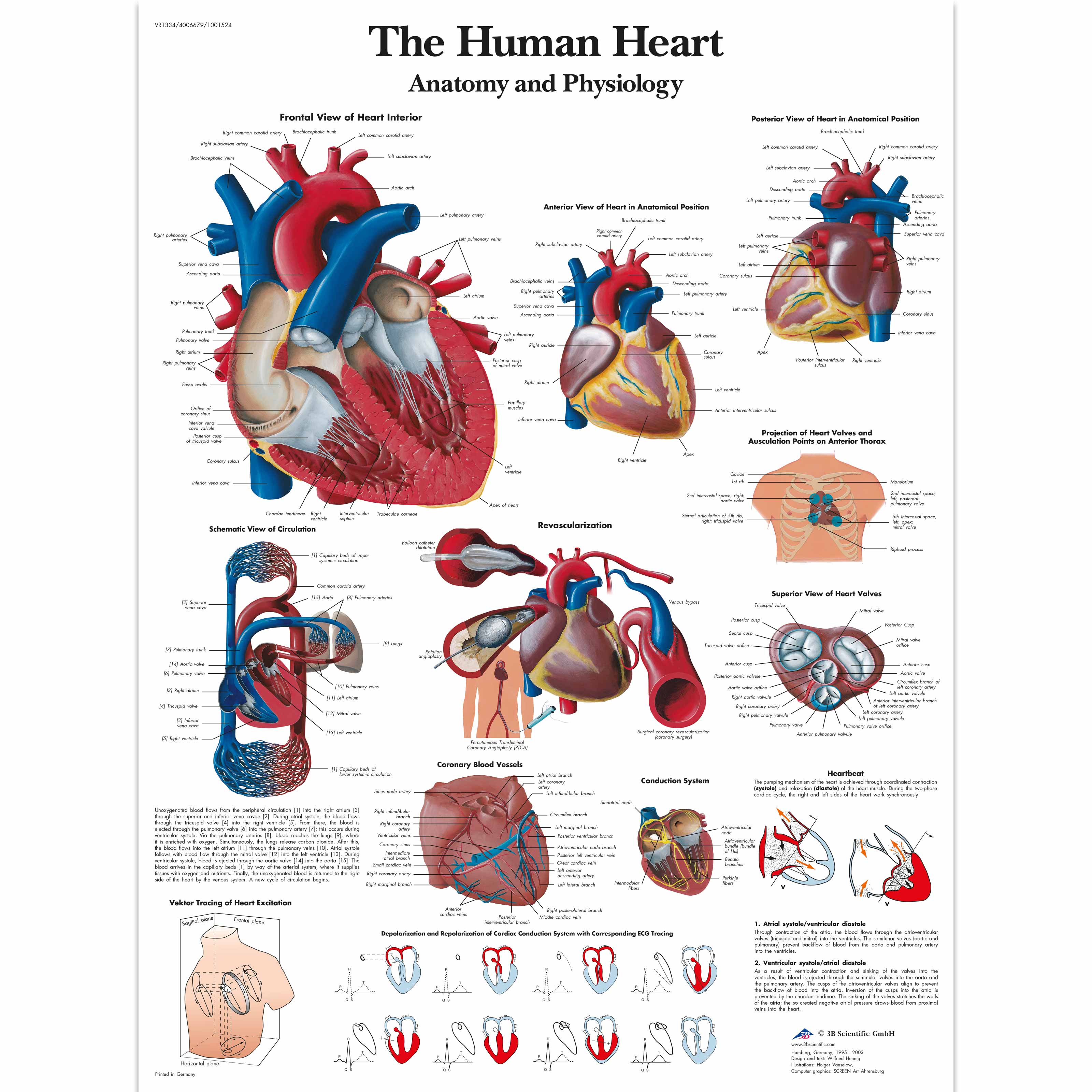
The Human Heart Chart Anatomy and Physiology 4006679 VR1334UU Cardiovascular System 3B
The heart is a muscular organ that serves to collect deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body, carries it to the lungs to be oxygenated and release carbon dioxide. Then, it transports the oxygenated blood from the lungs and distributes it to all the body parts. The heart pumps around 7,200 litres of blood in a day throughout the body.; The heart is situated at the centre of the chest and.

Human Heart Anatomy Diagram coordstudenti
Cardiac physiology is one of healthcare's most important aspects of medical knowledge. The cardiovascular system constantly adapts to maintain homeostasis in the body, specifically to maintain oxygen perfusion of tissues. The heart will adapt via multiple variables such as heart rate, stroke volume, preload, afterload, diastole, and systole.

Who loves cardiology?? I do I do I do oooooooh! (If you dont know that reference youre too yo
PowerPoint Presentation Cardiac Anatomy & Physiology Circulatory System The heart is a hollow muscular organ made of specialised cells that allow it to act as a pump within the circulatory system Cardiovascular and lymphatic systems make up the circulatory system a vast network of organs and vessels responsible for the flow of:

PPT Anatomy and Physiology of the Heart PowerPoint Presentation ID7043704
Heart anatomy. The heart has five surfaces: base (posterior), diaphragmatic (inferior), sternocostal (anterior), and left and right pulmonary surfaces. It also has several margins: right, left, superior, and inferior: The right margin is the small section of the right atrium that extends between the superior and inferior vena cava .

Human Heart Diagram and Anatomy of the Heart StudyPK Heart diagram, Anatomy of the heart
Anatomy, physiology and pharmacology of the autonomic supply of the heart. Anatomy, physiology and pharmacology of the autonomic supply of the heart. The Medulla control centre. The medulla is the primary site in the brain for regulating sympathetic and parasympathetic (vagal) outflow to the heart and blood vessels. 299 views • 13 slides

PPT Apparatus for the Analysis of Heart Sounds PowerPoint Presentation ID2963554
The heart is one of the most vital organs in the human body. Its role in sustaining life is paramount, as it pumps blood throughout the body, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to all the organs and tissues. But. why does it look nothing like the cute shape we always draw?

Anatomy of the Human Heart PowerPoint Shapes SlideModel
Pearson PowerPoints (fundamentals A&P 11th edition) — HCC Learning Web. Home. Faculty. Stephen Henry. Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 2301 (Martini text-Pearson) (2301 13978) Course Materials.
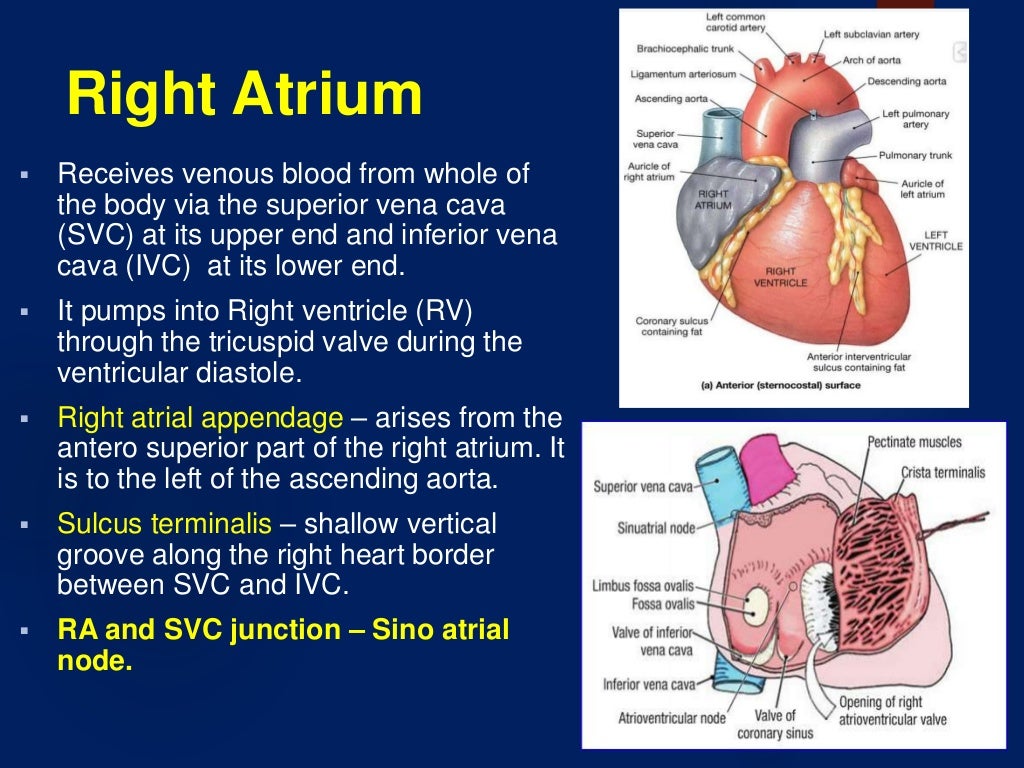
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE HEART
CPR. The position of the heart in the torso between the vertebrae and sternum (see Figure 19.2 for the position of the heart within the thorax) allows for individuals to apply an emergency technique known as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if the heart of a patient should stop. By applying pressure with the flat portion of one hand on the sternum in the area between the line at T4 and T9.