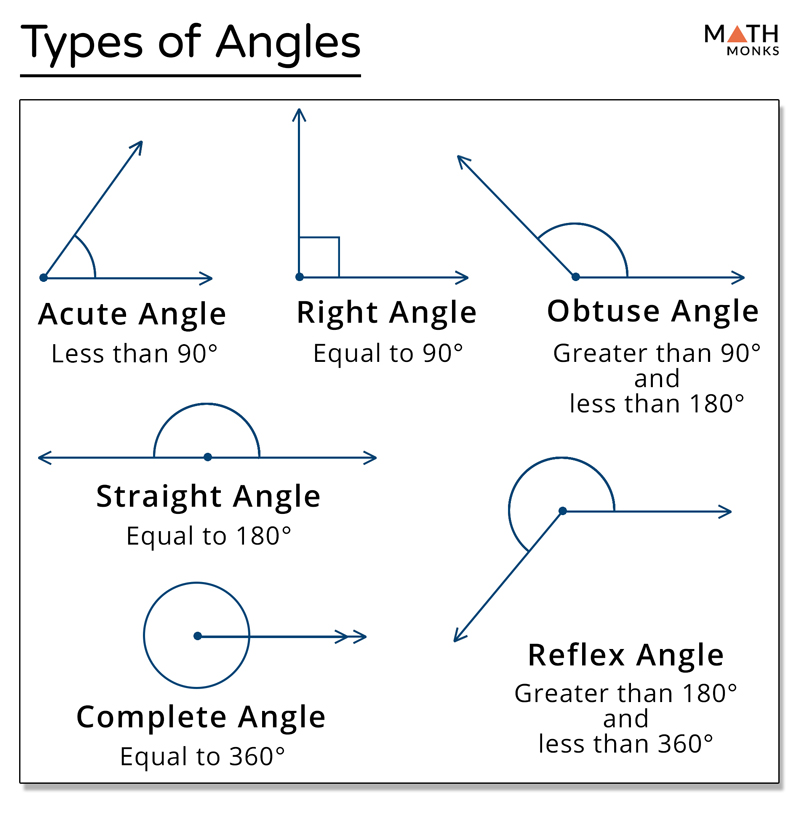
Angle Definition and Types with Examples
Unit 1 Lines Unit 2 Angles Unit 3 Shapes Unit 4 Triangles Unit 5 Quadrilaterals Unit 6 Coordinate plane Unit 7 Area and perimeter Unit 8 Volume and surface area Unit 9 Pythagorean theorem Unit 10 Transformations Unit 11 Congruence Unit 12 Similarity Unit 13 Trigonometry Unit 14 Circles Unit 15 Analytic geometry Unit 16 Geometric constructions
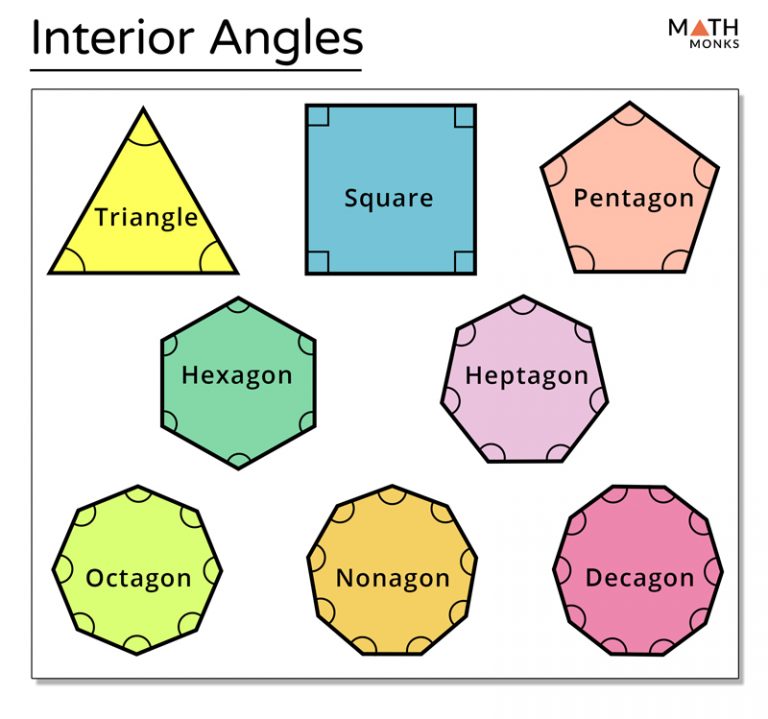
Interior and Exterior Angles Definitions & Formulas with Examples
Interior angles: Interior Angles are the angles formed within or inside a shape . Here, ∠ABC, ∠BCA and ∠CAB are interior angles. Exterior angles: Exterior angles are the angles formed outside a shape, between any side of a shape and an extended adjacent side. Here, ∠ACD is an exterior angle.

Geometry Resources Geometry Worksheets Printable Teaching Resources
Angles in polygons. We can calculate the interior and exterior angles of any polygon.. Interior angles; The sum of interior angles in any n -sided shape is determined using the formula, \text{Sum of interior angles}=180(n-2). One interior angle of a regular polygon with n -sides is determined using the formula, \theta=\frac{180(n-2)}{n}.

Right Angles in 2D Shapes DocsLib
Well for a shape like this, you can think of an angle as where two of the sides come together. So for example, this right over here is an angle because two of the sides have come together there, this side and this side come together at that point. So that's an angle. This is another angle. And that's another angle.
Angles KS2 — PlanBee
Save valuable time with this handy measuring angles worksheet. Help your children perfect their protractor use and get to grips with measuring angles. Protractors can be an intimidating tool for children at first. Ease them into the amazing world of angle measurement with these exercises. Your children will be asked to measure the angles of 6 common shapes, including a square, triangles and a.
Set of Different Degrees Angles. Geometric Mathematical Degree Angle
Key ideas The sum of the three angles in any triangle is 180°. The sum of the four angles in any quadrilateral is 360°. The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is 360°. The angle between a radius and the corresponding tangent to a circle is 90°.
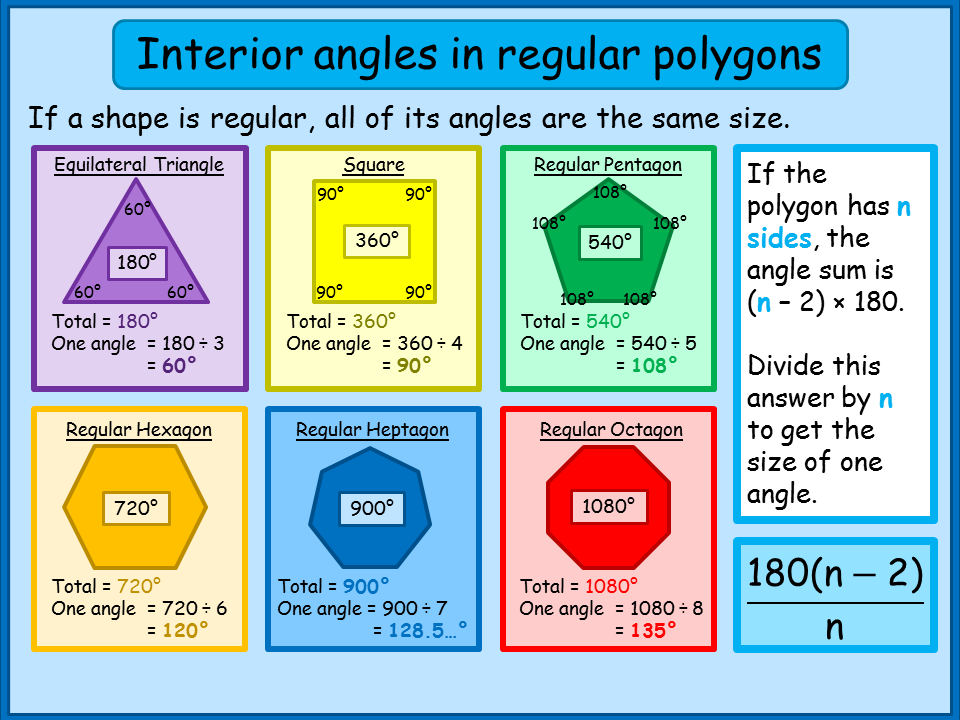
Interior Angles of Regular Polygons A Plus Topper
All three angles add up to 180\degree. So, the missing angles add up to. 180 \degree - 70 \degree = 110 \degree. An isosceles triangle has two equal angles, so the missing angles are both. 110 \degree \div 2 = 55 \degree

Types Of Angles Acute, Right, Obtuse, Straight, Reflex Angle
To identify angles inside 2D shapes. To recognise right angles. To recognise obtuse and acute angles. To revise angles. To identify perpendicular lines. To draw perpendicular lines. To identify and explain parallel lines. To revise parallel and perpendicular lines. To identify rectangles including squares.

17+ Different Angles In Geometry Tips GM
GCSE AQA Angles, lines and polygons - AQA Types of angle Polygons are multi-sided shapes with different properties. Shapes have symmetrical properties and some can tessellate. Part of Maths.
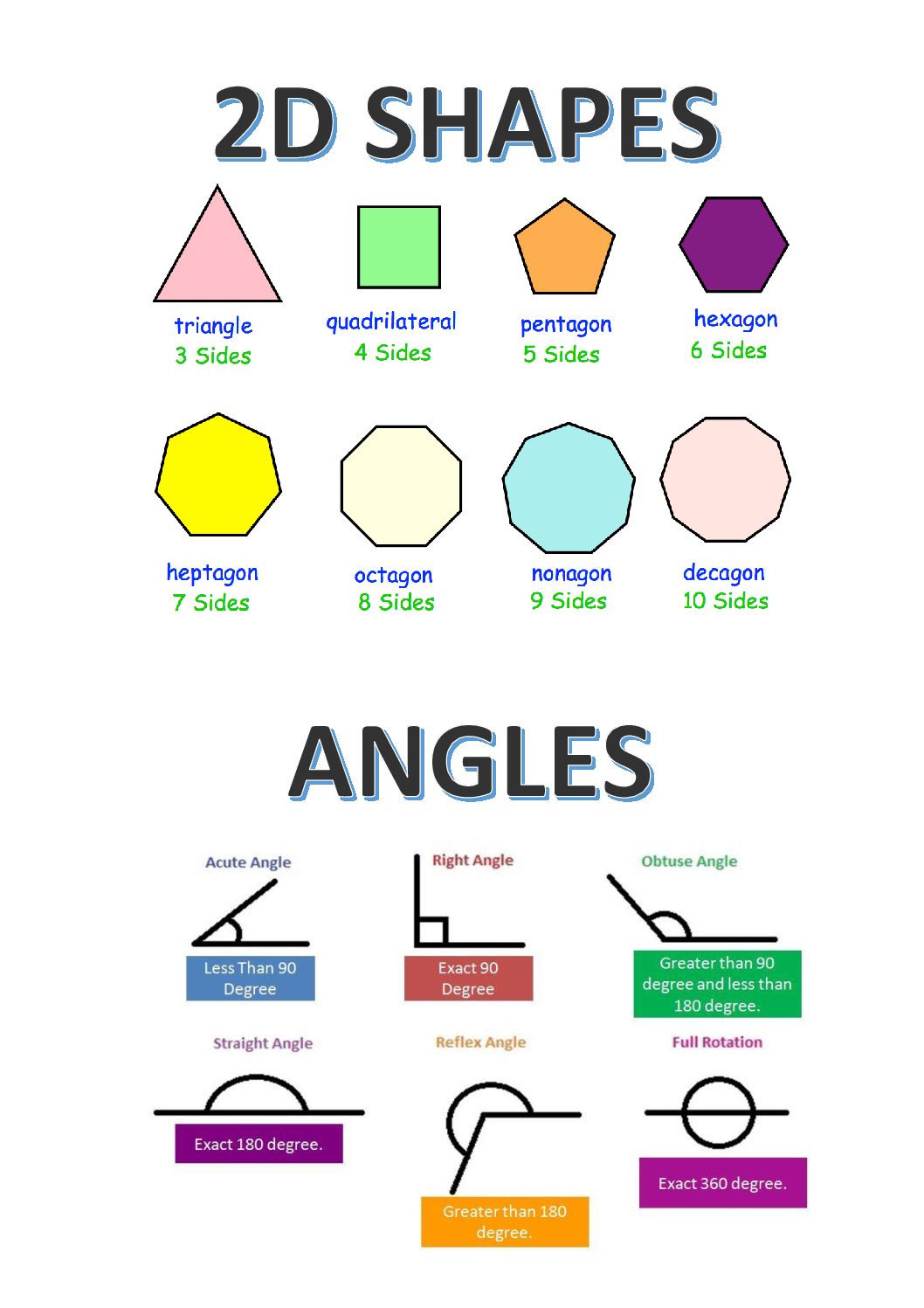
2D shapes and angles Teacha!
Video Transcript Nurse: A right angled formed when two objects are perpendicular to each other and it's like this, 90 degrees. Male nurse: A completely flat line would be 180 and then you'd go onto.

Right angles in a shape YouTube
Angles within a shape. In this lesson, we will learn how to recognise and draw angles within shapes, then understand statements about angles and properties of shapes. This quiz includes images that don't have any alt text - please contact your teacher who should be able to help you with an audio description.

2nd Grade Counting Angles in Shapes Made By Teachers
Classifying shapes by line and angles types (video) | Khan Academy 4th grade Course: 4th grade > Unit 11 Lesson 5: Classifying geometric shapes Classifying shapes by line and angles types Quadrilateral properties Classifying shapes by lines and angles Classify shapes by line and angle types Quadrilaterals review Math > 4th grade > Plane figures >
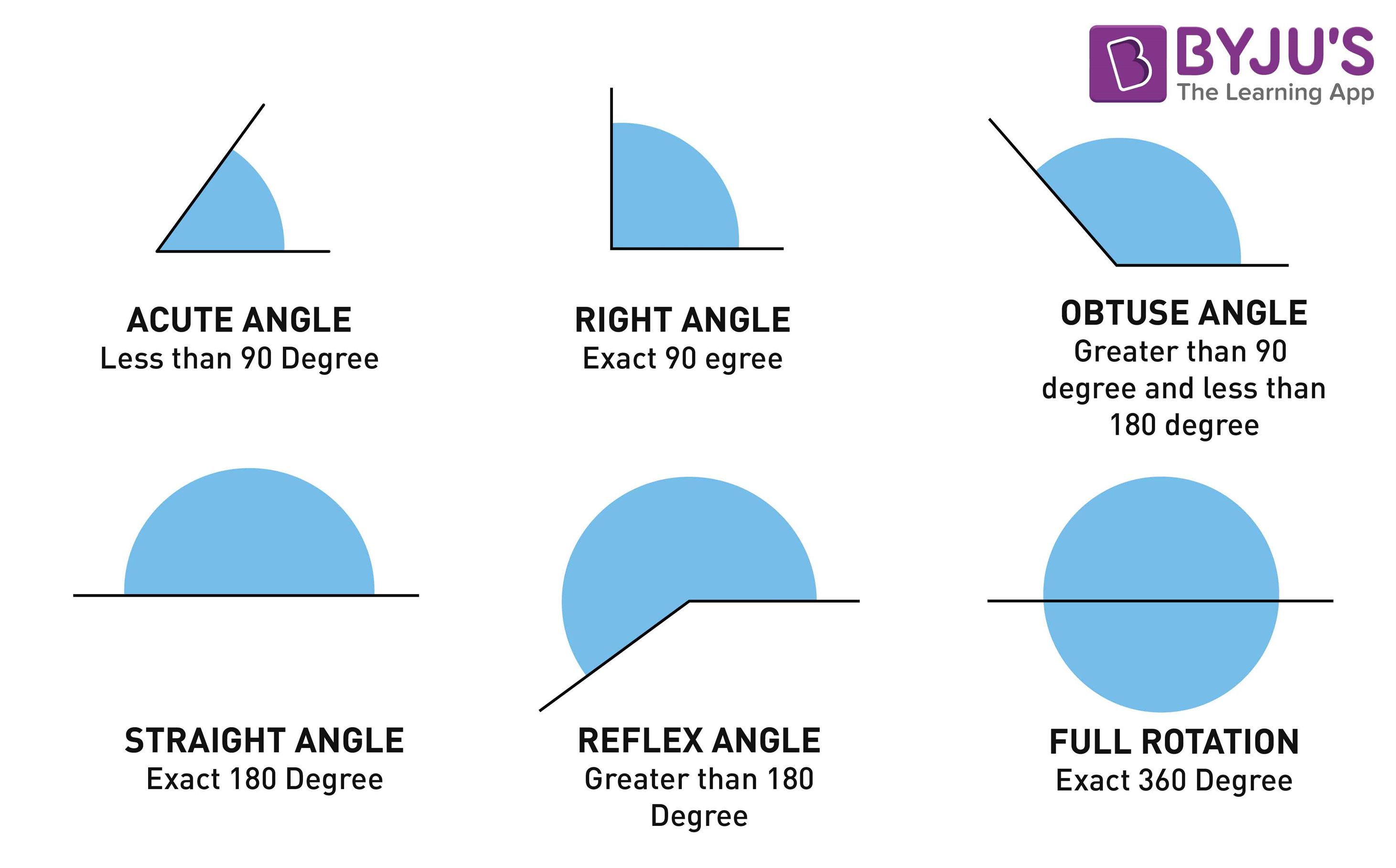
Types of Angles (Acute, Obtuse, Right, Straight, Reflex)
The General Rule Each time we add a side (triangle to quadrilateral, quadrilateral to pentagon, etc), we add another 180° to the total: So the general rule is: Sum of Interior Angles = ( n −2) × 180 ° Each Angle (of a Regular Polygon) = ( n −2) × 180 ° / n Perhaps an example will help: Example: What about a Regular Decagon (10 sides) ?

Shapes & Angles X, F and Z angles YouTube
Unit 1 Lines Unit 2 Angles Unit 3 Shapes Unit 4 Triangles Unit 5 Quadrilaterals Unit 6 Coordinate plane Unit 7 Area and perimeter Unit 8 Volume and surface area Unit 9 Pythagorean theorem Unit 10 Transformations Unit 11 Congruence Unit 12 Similarity Unit 13 Trigonometry Unit 14 Circles Unit 15 Analytic geometry Unit 16 Geometric constructions
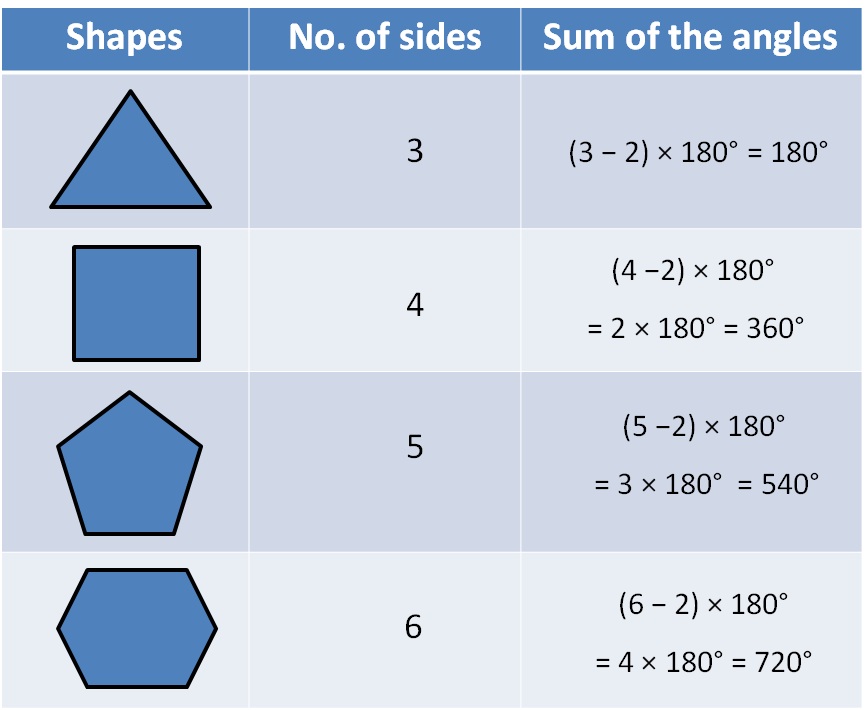
Angle sum property of polygons with formula Teachoo Polygons
Right angles in shapes (informal definition) Google Classroom Identify right angles in shapes. Introduction Many shapes have corners. We call a corner a right angle if we can fit a little square perfectly inside it. Consider the trapezoid Let's draw a square in each corner. In which corners did the little square fit perfectly?

Mr. Spaulding's Fourth Grade Class Classifying Angles
Angles of Polygons - Summary. Polygons are 2D shapes categorized as regular (with congruent sides and angles) or irregular. They have interior angles whose sum varies by shape: triangles 180°, quadrilaterals 360°. Exterior angles in all polygons sum up to 360°. Polygons with equal sides also have equal angles.